
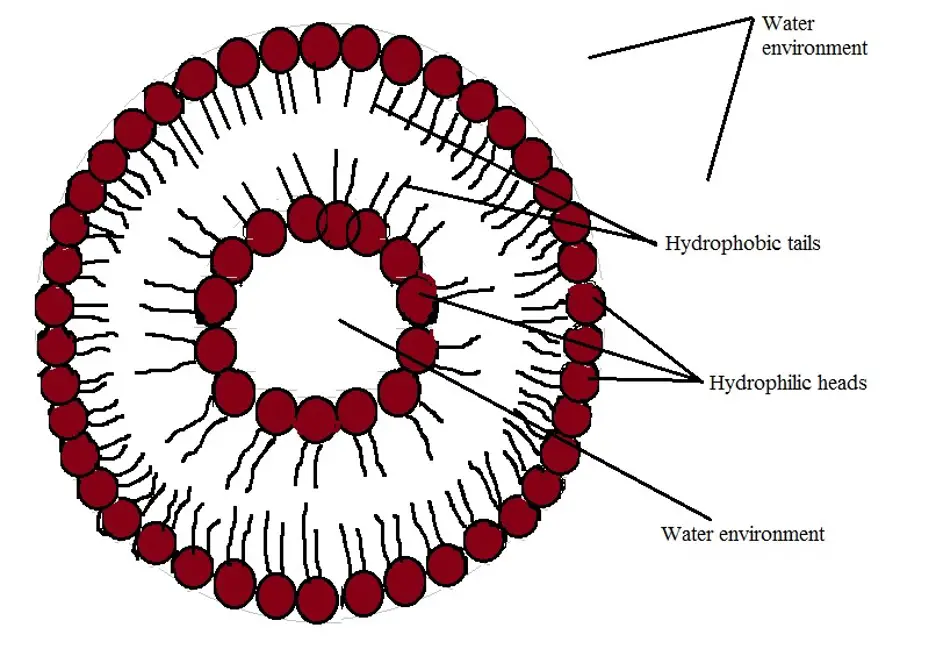
The two dark bands are the two leaflets comprising the bilayer. This “flaw” remained unanswered for nearly half a century until the discovery that specialized molecules called integral membrane proteins can act as ion transportation pumps.ĭiscovery of lipid bilayer structure Ī micrograph from a Transmission Electron Micrograph showing a lipid vesicle.
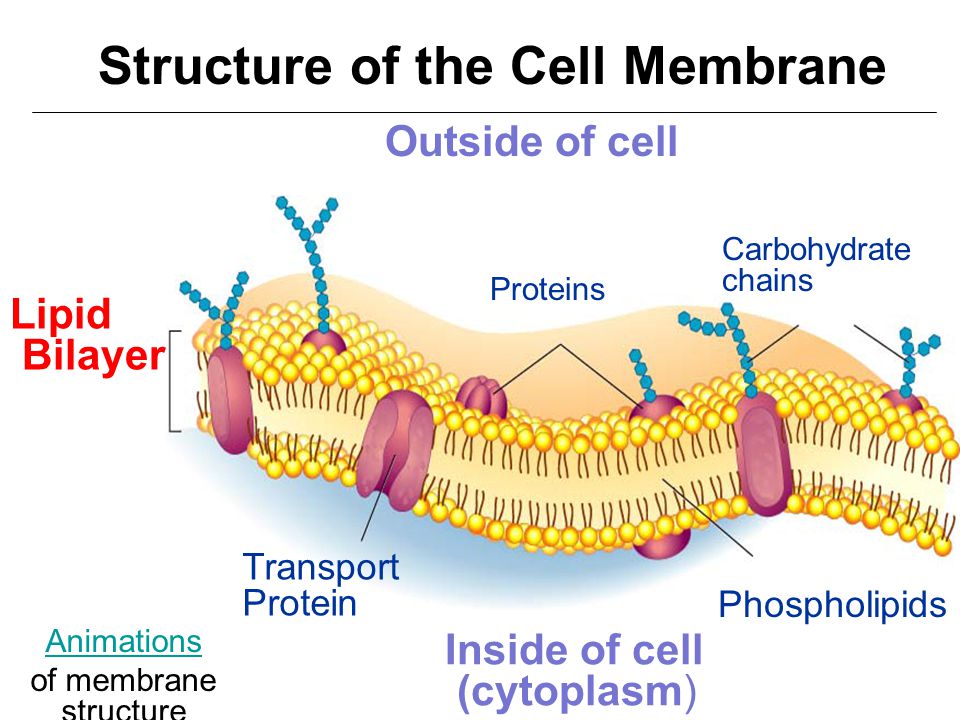
One of the early criticisms of this theory was that it included no mechanism for energy-dependent selective transport. They interpreted this as meaning that to pass the cell membrane a molecule must be at least sparingly soluble in oil, their “lipoid theory of narcosis.” Based on this evidence and further experiments, they concluded that the cell membrane might be made of lecithin ( phosphatidylcholine) and cholesterol. Hans Horst Meyer and Ernest Overton independently noticed that the chemicals which act as general anesthetics are also those soluble in both water and oil. This theory was further extended by evidence from the study of anesthetics. Based on these observations, Quincke asserted that the cell membrane comprised a fluid layer of fat less than 100 nm thick. He also noted that a thin film of oil behaves as a semipermeable membrane, precisely as predicted.

The only other known material to exhibit this behavior was oil. The lipid nature of the cell membrane was first correctly intuited by Georg Hermann Quincke in 1888, who noted that a cell generally forms a spherical shape in water and, when broken in half, forms two smaller spheres. Traube had no direct evidence for the composition of this film, though, and incorrectly asserted that it was formed by an interfacial reaction of the cell protoplasm with the extracellular fluid. By the mid 19th century, this question was being actively investigated and Moritz Traube noted that this outer layer must be semipermeable to allow transport of ions. The plant cell wall was easily visible even with these early microscopes but no similar barrier was visible on animal cells, though it stood to reason that one must exist. Since the invention of the microscope in the seventeenth century it has been known that plant and animal tissue is composed of cells : the cell was discovered by Robert Hooke. Cork was one of the first substances examined by Robert Hooke through his microscope and he found that it was composed of thousands of minute pockets he named "cells".


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
